本科学过c++的数据结构了,但研究生转无线通信后就忘的差不多了,现在重新复习下栈。
栈(stack)、队列(queues)、双端队列(deques)和列表都是有序数据容器,元素添加后在容器内的位置跟其他元素添加和删除的顺序有关,像这样的容器被称作线性数据结构(linear data structure)。
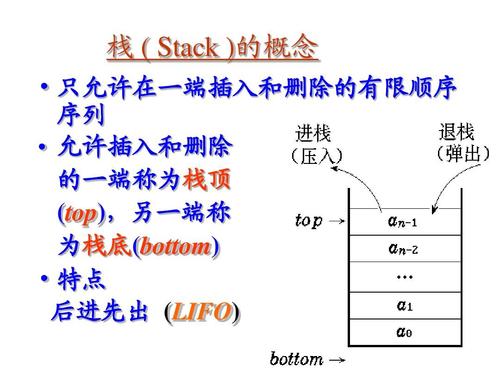
栈可以想象为只有一端开口的瓶子,假设每放一个东西进去都会把前面放的完全盖住,那么这时你想取出最里面的东西显然是不可能的,所以你只能把上面的一个个拿出来才能取到你想要的,这就叫做后进先出(LIFO, last-in first-out)。
1. 栈的主要方法及实现
栈的方法主要有下面几种:
Stack()creates a new stack that is empty. It needs no parameters and returns an empty stack.push(item)adds a new item to the top of the stack. It needs the item and returns nothing.pop()removes the top item from the stack. It needs no parameters and returns the item. The stack is modified.peek()returns the top item from the stack but does not remove it. It needs no parameters. The stack is not modified.isEmpty()tests to see whether the stack is empty. It needs no parameters and returns a boolean value.size()returns the number of items on the stack. It needs no parameters and returns an integer.
在python中是没有栈的实现的,所以栈需要自己实现,简单点可以用个list充当下,更一般的要实现上面各种方法还是面向对象创造一个类比较好,实现代码如下所示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def isEmpty(self):
return self.items == []
def push(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def pop(self):
return self.items.pop()
def peek(self):
return self.items[len(self.items)-1]
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
2. 栈的主要应用
2.1 字符串反转
那么,费尽心机创造一个栈有啥用呢?首先可以用来翻转字符串,当然python有超级多方式可以反转字符串,最简单的自然是string[::-1]。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8def stringReverse(self, stringstring):
s = Stack()
output = ""
for ss in stringstring:
s.push(ss)
while not s.isEmpty():
output = output + s.pop()
return output
2.2 简单括号匹配
除此之外,还有简单的括号匹配问题,也可以利用栈的特性来解决:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20def parChecker(symbolString):
s = Stack()
balanced = True
index = 0
while index < len(symbolString) and balanced:
symbol = symbolString[index]
if symbol == "(":
s.push(symbol)
else:
if s.isEmpty():
balanced = False
else:
s.pop()
index = index + 1
if balanced and s.isEmpty():
return True
else:
return False
其实吧,也可以不用栈解决呀(不是我杠,笔试时间也是很重要的)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9def parChecker(symbolString):
left = 0
right = 0
for s in symbolString:
if s == '(':
left+=1
else:
right+=1
return left==right
2.3 多重括号匹配
拓展到更复杂一点的括号匹配问题——多重括号匹配:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25def parChecker(symbolString):
s = Stack()
balanced = True
index = 0
while index < len(symbolString) and balanced:
symbol = symbolString[index]
if symbol in "([{":
s.push(symbol)
else:
if s.isEmpty():
balanced = False
else:
top = s.pop()
if not matches(top,symbol):
balanced = False
index = index + 1
if balanced and s.isEmpty():
return True
else:
return False
def matches(open,close):
opens = "([{"
closers = ")]}"
return opens.index(open) == closers.index(close)
当然,我又“杠”了,主要不想想这么复杂的结构2333:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16def parChecker(symbolString):
l1,l2,l3,r1,r2,r3=0,0,0,0,0,0
for s in symbolString:
if s=='{':
l1+=1
elif s=='}':
r1+=1
elif s=='(':
l2+=1
elif s==')':
r2+=1
elif s=='[':
l3+=1
else:
r3+=1
return [l1,l2,l3]==[r1,r2,r3]
2.4 将十进制数转换为各种进制
想将10进制数(Decimal)转换为2进制(Binary)、8进制(Octal)或者16进制(Hexidecimal),就将这个数不断除进制数,然后将余数逆序输出,不想贴图了自己百度查下。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14def baseConverter(decNumber,base):
digits = "0123456789ABCDEF"
remstack = Stack()
while decNumber > 0:
rem = decNumber % base
remstack.push(rem)
decNumber = decNumber // base
newString = ""
while not remstack.isEmpty():
newString = newString + digits[remstack.pop()]
return newString
2.5 中缀表达式、前后缀表达式
接下来就是栈的重点操作了(就是比较复杂一点)。
什么是中缀表达式呢?就是一般的表达式,比如A+B, C*D等。
顾名思义,前缀表达式就是操作符在前面,后缀就是在后面,给几个例子体会一下:
Infix Expression Prefix Expression Postfix Expression
A + B C + D + + A B C D A B C + D +
(A + B) (C + D) + A B + C D A B + C D +
A B + C D + A B C D A B C D +
A + B + C + D + + + A B C D A B + C + D +
将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,利用栈可以写为:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30def infixToPostfix(infixexpr):
prec = {}
prec["*"] = 3
prec["/"] = 3
prec["+"] = 2
prec["-"] = 2
prec["("] = 1
opStack = Stack()
postfixList = []
tokenList = infixexpr.split()
for token in tokenList:
if token in "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" or token in "0123456789":
postfixList.append(token)
elif token == '(':
opStack.push(token)
elif token == ')':
topToken = opStack.pop()
while topToken != '(':
postfixList.append(topToken)
topToken = opStack.pop()
else:
while (not opStack.isEmpty()) and \
(prec[opStack.peek()] >= prec[token]):
postfixList.append(opStack.pop())
opStack.push(token)
while not opStack.isEmpty():
postfixList.append(opStack.pop())
return " ".join(postfixList)
假如直接给你一个后缀表达式让你计算呢,这就是需要再写一个算法了,不过比较简单,贴上来:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23def postfixEval(postfixExpr):
operandStack = Stack()
tokenList = postfixExpr.split()
for token in tokenList:
if token in "0123456789":
operandStack.push(int(token))
else:
operand2 = operandStack.pop()
operand1 = operandStack.pop()
result = doMath(token,operand1,operand2)
operandStack.push(result)
return operandStack.pop()
def doMath(op, op1, op2):
if op == "*":
return op1 * op2
elif op == "/":
return op1 / op2
elif op == "+":
return op1 + op2
else:
return op1 - op2
栈就目前学完了,后续有的话还会补充。